Coverage collection
This page covers coverage calculated on TVM assembly instructions. Path- and source-line coverage is not implemented.
@ton/sandbox tests.
Easy way
Library compatibilityFor this way to work correctly, version of @ton/sandbox >= 0.37.2 and @ton/blueprint >= 0.41.0 is needed.
blueprint test --coverage
coverage/ directory as HTML files with reports for each of your contracts.
Customizable way
There might be some reasons why you don’t want to simply use --coverage.
- You don’t want to collect coverage for all contracts.
- You use
@ton/sandbox but don’t use @ton/blueprint.
- Not all contracts have source code. (For example, for each transaction you deploy a new contract, and you don’t have wrappers for it).
- You want to get the raw data and customize the output.
1. Enable coverage collection
Before running tests, add blockchain.enableCoverage() to collect coverage data:
import {Blockchain} from '@ton/sandbox';
describe('Contract Tests', () => {
let blockchain: Blockchain;
let contract: SandboxContract<MyContract>;
beforeEach(async () => {
blockchain = await Blockchain.create();
blockchain.enableCoverage();
// or for COVERAGE=true mode only
// blockchain.enableCoverage(process.env["COVERAGE"] === "true");
// Deploy your contract
contract = blockchain.openContract(MyContract.fromInit());
// ... deployment logic
});
// Your tests here...
});
2. Collect coverage after tests
afterAll(() => {
const coverage = blockchain.coverage(contract);
console.log(coverage?.summary());
})
3. Generate reports
import {writeFileSync} from 'fs';
afterAll(() => {
const coverage = blockchain.coverage(contract);
if (!coverage) return;
// Generate HTML report for detailed analysis
const htmlReport = coverage.report("html");
writeFileSync("coverage.html", htmlReport);
// Print text text report to console
const textReport = coverage.report("text");
console.log(textReport);
});
Understanding coverage data
Coverage summary
The coverage summary provides key metrics about your test coverage:
const summary = coverage.summary();
console.log(`Total lines: ${summary.totalLines}`);
console.log(`Covered lines: ${summary.coveredLines}`);
console.log(`Coverage percentage: ${summary.coveragePercentage.toFixed(2)}%`);
console.log(`Total gas consumed: ${summary.totalGas}`);
console.log(`Total hits: ${summary.totalHits}`);
// Instruction-level statistics
summary.instructionStats.forEach(stat => {
console.log(`${stat.name}: ${stat.totalHits} hits, ${stat.totalGas} gas, avg ${stat.avgGas}`);
});
Coverage reports
- HTML Report: Interactive report with highlighting and line-by-line coverage details
- Text Report: Console-friendly report with coverage information and marked code
Advanced usage patterns
Multiple test suites
When running multiple test files, you might want to merge coverage data:
// In first test file
const coverage1 = blockchain.coverage(contract);
if (!coverage1) return;
const coverage1Json = coverage1.toJson();
writeFileSync("coverage1.json", coverage1Json);
// In second test file
const coverage2 = blockchain.coverage(contract);
if (!coverage2) return;
const coverage2Json = coverage2.toJson();
writeFileSync("coverage2.json", coverage2Json);
// Merge coverage data in separate script after tests
const savedCoverage1 = Coverage.fromJson(readFileSync("coverage1.json", "utf-8"));
const savedCoverage2 = Coverage.fromJson(readFileSync("coverage2.json", "utf-8"));
const totalCoverage = savedCoverage1.mergeWith(savedCoverage2);
console.log(`Combined coverage: ${totalCoverage.summary().coveragePercentage}%`);
Coverage for multiple contracts
When testing systems with multiple contracts:
describe('Multi-Contract System', () => {
let blockchain: Blockchain;
let contract1: SandboxContract<Contract1>;
let contract2: SandboxContract<Contract2>;
beforeEach(async () => {
blockchain = await Blockchain.create();
blockchain.enableCoverage();
// Deploy multiple contracts
contract1 = blockchain.openContract(Contract1.fromInit());
contract2 = blockchain.openContract(Contract2.fromInit());
});
afterAll(() => {
// Get coverage for each contract separately
const coverage1 = blockchain.coverage(contract1);
const coverage2 = blockchain.coverage(contract2);
if (!coverage1 || !coverage2) return;
console.log('Contract 1 Coverage:', coverage1.summary().coveragePercentage);
console.log('Contract 2 Coverage:', coverage2.summary().coveragePercentage);
// Generate separate reports
writeFileSync("contract1-coverage.html", coverage1.report("html"));
writeFileSync("contract2-coverage.html", coverage2.report("html"));
});
});
Interpret results
The usual report looks like this:
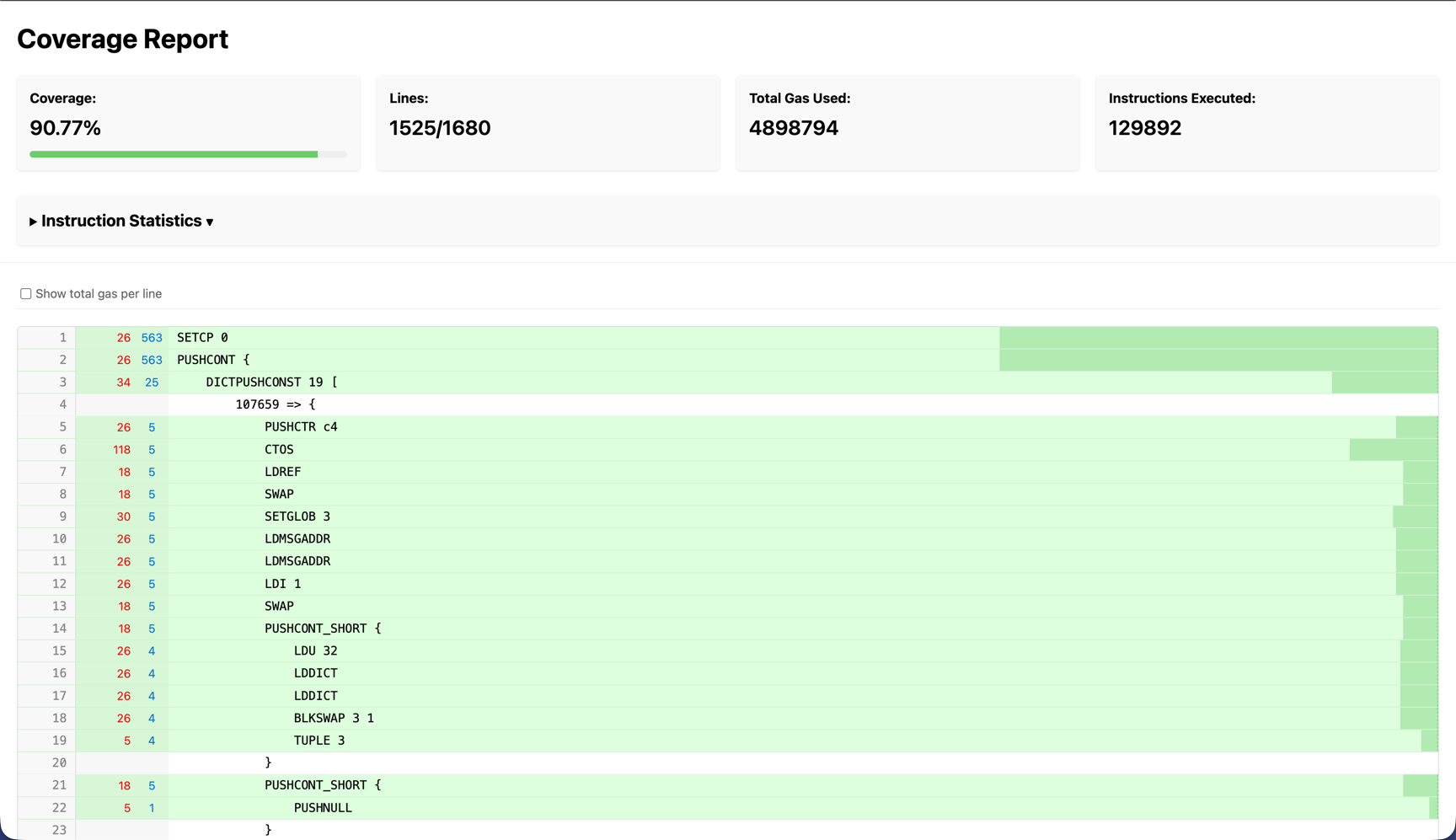
 Apart from the header statistics, the line-by-line coverage report is the most informative. Most fields are self‑explanatory; the code section shows per‑instruction hit counts (blue) and gas cost (red). This helps you analyze both coverage and gas efficiency.
Apart from the header statistics, the line-by-line coverage report is the most informative. Most fields are self‑explanatory; the code section shows per‑instruction hit counts (blue) and gas cost (red). This helps you analyze both coverage and gas efficiency.
To understand the TVM assembly output, read TVM. Limitations
Note that when code of other contracts is stored directly in the code of contract (Tact does that automatically if a contract system does not contain circular dependencies), that affects the overall code coverage percentage.
To mitigate this effect in coverage estimation, add a circular dependency. For example, import a file with the following content.
contract A {
receive() {
let x = initOf B();
drop2(x);
}
}
contract B(
) {
receive() {
let x = initOf A();
drop2(x);
}
}
asm fun drop2(x: StateInit) {
DROP2
}

 Apart from the header statistics, the line-by-line coverage report is the most informative. Most fields are self‑explanatory; the code section shows per‑instruction hit counts (blue) and gas cost (red). This helps you analyze both coverage and gas efficiency.
Apart from the header statistics, the line-by-line coverage report is the most informative. Most fields are self‑explanatory; the code section shows per‑instruction hit counts (blue) and gas cost (red). This helps you analyze both coverage and gas efficiency.